Uniswap v4 is here. The ecosystem has come a long way since 2018, having matured from operating as a simple automated market maker. With v4, Uniswap has simplified processes, is cheaper, and more flexible for decentralized finance (DeFi) degens and users. So what exactly does v4 bring to the table, and how does it compare to previous versions? This guide covers everything you need to know about the latest version of the decentralized exchange in 2025.
In this guide:
- What is Uniswap v4: How is it different?
- Uniswap v4 vs. other versions
- Uniswap v4 features: A deep dive
- Who should switch to Uniswap v4?
- How do pools work in Uniswap?
- The current state of Uniswap v4
- Uniswap v4 versus older versions
- Frequently asked questions
What is Uniswap v4: How is it different?
Uniswap v4 is the latest upgrade to the world’s largest decentralized exchange, designed to cut trading costs, improve efficiency, and give users more control over liquidity and fees.
Uniswap v4 is the talk of the DeFi town in 2025. Here is a quick overview of all the new features it packs:
- Much lower gas fees – Up to 99.99% cheaper to create liquidity pools.
- Hooks – Developers can customize trading logic (like dynamic fees & limit orders).
- Flash accounting – Cuts down on unnecessary token transfers, saving gas fees.
- Dynamic fees – Pools can adjust fees automatically based on market conditions.
- Native ETH support – No more wrapping ETH into WETH before trading.
- Singleton contract – Uniswap v4 manages all pools under one contract, which lowers complexity by several notches.
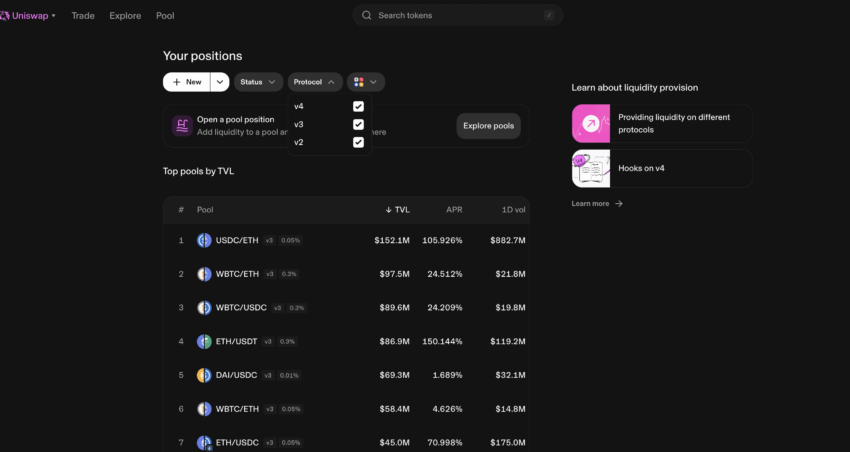
Creating Uniswap V4 positions: Uniswap
Uniswap v4 vs. other versions
Here’s a quick rundown of the features each previous version introduced.
Uniswap v1 (2018)
- First-ever decentralized automated market maker (AMM).
- ETH was required as the bridge for every trade (no direct token-to-token swaps).
- No price oracles, no advanced trading strategies — just a basic swap system.
Uniswap v2 (2020)
- Direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 trading (ETH no longer needed as a bridge).
- Flash swaps — users can borrow assets without upfront collateral.
- Introduced price oracles, making swaps more secure.
Uniswap v3 (2021)
- Concentrated liquidity — liquidity providers (LPs) could choose price ranges for their funds.
- Multiple fee tiers (0.05%, 0.3%, 1%) for better market efficiency.
- More capital-efficient but expensive due to separate pool contracts.
Uniswap versions compared
Uniswap versions compared
All versions available: Uniswap
Uniswap v4 features: A deep dive
In the following sections, we will look more closely into each new trait.
The biggest change: The Singleton contract
Before (v3): Every new liquidity pool required a separate smart contract, making transactions more expensive.
Now (v4): One big contract (Singleton Design) handles all pools under one roof, significantly reducing gas fees.
Uniswap v4 pools with relatively low liquidity: Uniswap
The key concepts have of course already been memed:
Hooks
Before (v3): Uniswap’s logic was fixed — trades followed a set pattern, and liquidity providers had limited control.
Now (v4): Developers can add custom trading rules using Hooks.
Uniswap V4 swap mechanism: Uniswap blog
Hooks allow you to:
- Set dynamic fees that adjust automatically during high volatility.
- Create limit orders so a swap only happens when the price is right.
- Auto-reinvest LP rewards without manual intervention.
What’s up with Flash Accounting?
Before (v3): Every time you swap tokens, Uniswap transfers tokens back and forth multiple times per trade.
Now (v4): Uniswap keeps track of all balance changes internally and only transfers the final amount, cutting down gas fees.
Dynamic fees
This feature brings smarter pricing for swaps. Here are the differences:
Before (v3): Pools had fixed fees (0.05%, 0.3%, 1%), meaning LPs couldn’t adjust based on market trends.
Now (v4): Fees can increase during high volatility and decrease during calm periods, optimizing LP earnings.
Native ETH support
Before (v3): You had to wrap ETH into WETH before trading.
Now (v4): You can trade with native ETH, saving extra gas fees & simplifying transactions.
Better liquidity management with Subscribers
Before (v3): If you wanted extra rewards for providing liquidity, you had to stake your position, meaning you temporarily gave up control.
Now (v4): Subscribers let you earn rewards without giving up control of your funds.
Who should switch to Uniswap v4?
You can consider using v4:
- If you’re a trader: You get lower gas fees, native ETH support, and more efficient swaps.
- If you’re a liquidity provider: You can optimize your liquidity with hooks and earn better rewards with dynamic fees.
- If you’re a developer: You gain full control over trading strategies with custom hooks.
Or, if you’re looking for an alternative to Uniswap entirely, the below X posts sets out a few options.
How do pools work in Uniswap?
If you’ve used Uniswap before, you’ve interacted with liquidity pools — but you might not know how they work behind the scenes.
How pools worked in Uniswap v3 vs. v4
Before (v3): Every single trading pair had its own separate smart contract, meaning if you wanted to trade across multiple pools, Uniswap had to interact with multiple contracts, increasing gas fees and slowing things down.
Now (v4): Pools don’t live in separate contracts anymore. Instead, they all exist inside one big contract called the PoolManager.
This means:
- Creating a new pool is up to 99.99% cheaper compared to previous versions — because you’re not deploying an entire new contract.
- Multi-hop swaps (swapping through multiple pools) are far cheaper — because tokens don’t have to move around so much.
- All pools are managed in one place, making everything faster and more efficient.
Also, v3 left another issue to solve — how tokens move within pools. Every trade or liquidity adjustment in previous versions required multiple ERC-20 transfers, which increased gas costs unnecessarily.
Operating pools: Uniswap
ERC-6909: A more gas-efficient token system for pools
In Uniswap v4, the protocol has upgraded from ERC-1155 to ERC-6909 to optimize token claims, redemptions, and liquidity positions.
Now, Uniswap v4 introduces ERC-6909, a lighter and more gas-efficient token standard that helps liquidity providers and traders save on fees by reducing unnecessary external calls.
What this means for liquidity providers and traders:
- Lower gas fees when providing or removing liquidity.
- More efficient liquidity management — LPs don’t need to move ERC-20 tokens every time they interact with the pool.
- High-frequency traders and liquidity managers benefit the most since they avoid costly ERC-20 approvals and transfers.
The current state of Uniswap v4
Yes, Uniswap v4 is live. But there is more happening in the background:
- v4 is deployed on 10+ blockchains, including Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, OP Mainnet, Base, BNB Chain, Blast, World Chain, Avalanche, and Zora Network.
- Liquidity is still migrating — many traders are still using v3 pools, but new liquidity is being added to v4 every day. Pools might be available in time.
- Swaps are being routed across v2, v3, and v4 through UniswapX, which automatically finds the best price for you.
Supported blockchains: Uniswap v4
Note: If you’re swapping, you don’t have to do anything — Uniswap automatically routes your trade to the best pool (whether it’s v2, v3, or v4). Also, if you’re providing liquidity, you now have a choice. You can stick to v3 if you like, or migrate to v4 for lower gas costs and increased customization options.
Uniswap v4 versus older versions
Uniswap v4 brings cheaper transactions, more flexibility, and advanced features, making it the best choice for most users moving forward. However, v3 still holds an edge in deep liquidity, and some traders and LPs may prefer its fixed fee structures and established ecosystem. For now, v4 is the future, but v3 and v2 still serve specific needs, so your decision should be based on your trading style and liquidity strategy.
Read the full article here